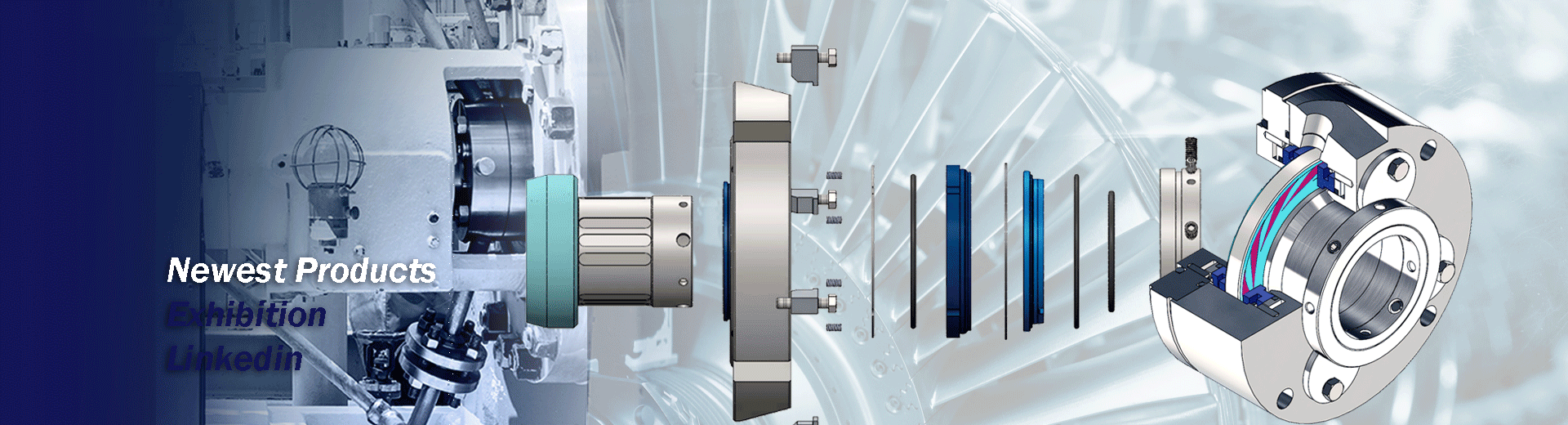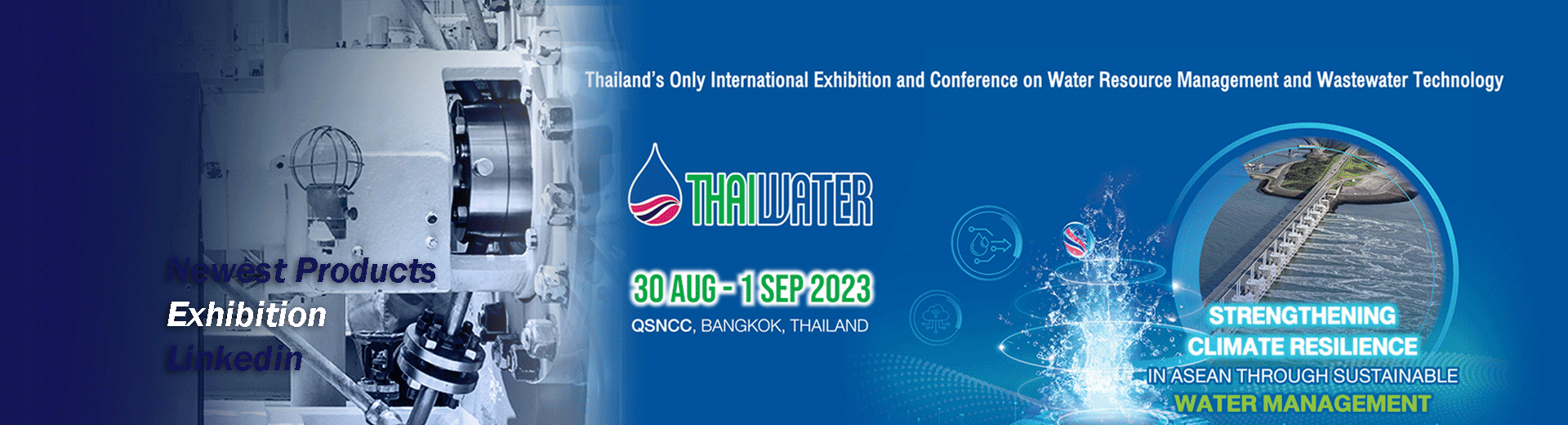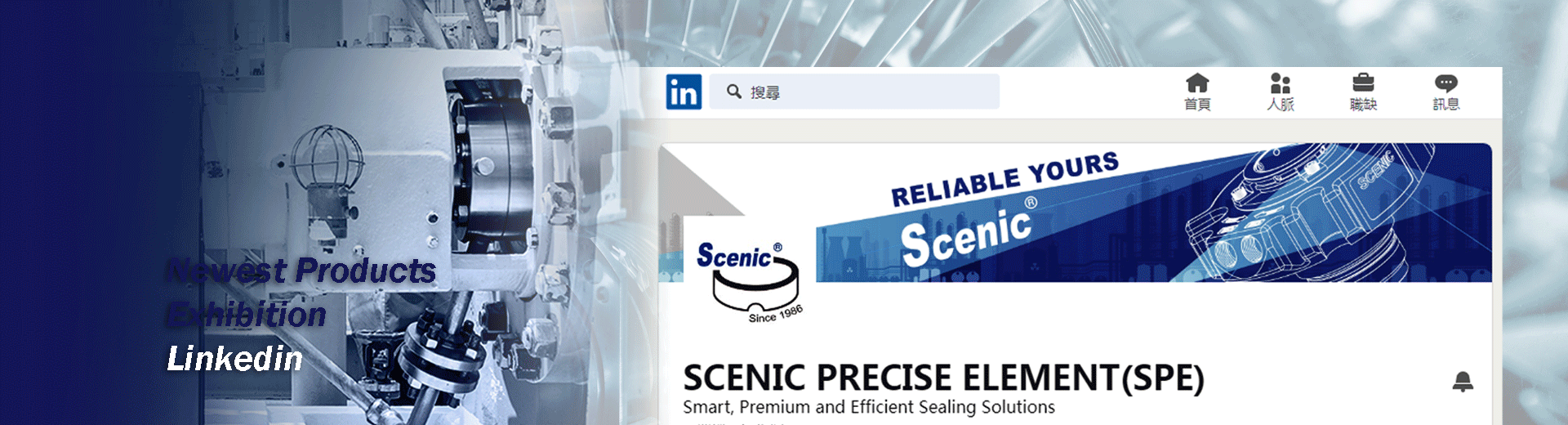
What is Mechanical Seal?
The sealing part for rotating equipment, preventing fluid leakage and VOC emissions
Before we start, the first thing to verify is that why do we need a mechanical seal? The mechanical shaft seal is commonly positioned at the core of rotating machinery, primarily aimed at preventing the escape of pressure or gases from the internal workings of the equipment to the surrounding environment. It also serves to safeguard against external contaminants infiltrating the internal components, particularly crucial when dealing with fluids containing hazardous substances like Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). This technology boasts widespread applications spanning diverse sectors such as chemical processing, petrochemicals, energy production, manufacturing, and various other industries.Mechanical shaft seals play an integral role in modern industrial processes. While their costs during the plant construction phase typically represent a relatively small percentage, usually not exceeding 3% of the total expenses, they transform into crucial components once the equipment is operational. They significantly influence the production efficiency and safety of an entire factory. These seals ensure the smooth operation of rotating machinery while shielding operational personnel from potential occupational hazards. If a mechanical shaft seal malfunctions or fails to achieve the expected sealing performance, it could potentially cause severe adverse effects on the overall operation of the factory.
What is the Principle of Mechanical Seal?
Key Sealing Technology Comprising Rotating and Stationary Rings
A mechanical shaft seal generally consists of two primary parts: the Rotary Section and the Stationary Section. The rotary section is typically mounted on the rotating shaft, while the stationary section remains attached to the stationary machine casing. As the shaft rotates, a sealing interface forms between the rotating and stationary parts, ensuring that fluids or gases within the equipment do not leak externally.The operation of a mechanical shaft seal is based on the application of pressure, creating a sealing surface between the rotating and stationary parts. This pressure is achieved through a combination of springs, pressure plates, or pressure levels, maintaining a tight contact to prevent fluid or gas leakage. Additionally, to minimize wear and heat generation at the sealing interface, lubricants such as oil or grease are often introduced between the sealing surfaces.

Structural Determinants of Durability
A mechanical seal represents a highly precise dynamic mechanical structure with intricate internal architecture involving various engineering principles, including fluid dynamics and thermodynamics. This complex structure plays a critical role in ensuring that there are no fluid leaks during the operation of rotating equipment. Hence, the structural design of a mechanical shaft seal directly impacts its durability and performance.A durable mechanical shaft seal design incorporates dedicated channels or pathways for fluids to minimize friction between the seal and the fluids during equipment operation. This reduction in friction helps decrease wear and waste heat, potentially enabling self-cooling effects, extending the seal's lifespan, maintaining equipment operation, and reducing energy consumption.
Material Determining Adaptability
The choice of materials for a mechanical shaft seal is a crucial factor in determining its performance and durability. This selection process involves considerations of various environmental factors, including the fluid's pH, impurity content, temperature, and pressure. Different operating environments demand different materials. Here are some commonly used materials for mechanical shaft seals based on specific components:- Metal Components/Internal Liquid Contact Parts: Stainless Steel SUS304, SUS316 / Titanium (Ti) / Hastelloy C (C-276) / Duplex Stainless Steel / Monel
- Stationary Rings: Carbon Graphite / Silicon Carbide / Tungsten Carbide
- Rotating Rings: Silicon Carbide / Tungsten Carbide
- Rubber O-rings: Perfluoroelastomer FFKM (Chemraz / Kalrez / SceniRAZ) / Fluoroelastomer FKM / AFLAS / Nitrile Rubber NBR / Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer EPDM / Tetrafluoroethylene-propylene TV / Hiflour
- Springs: Stainless Steel SUS316 / Hastelloy C (C-276) / Inconel
The selection of materials needs to be tailored to the specific operational conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the mechanical shaft seal. Factors such as resistance to chemicals, temperature variations, and mechanical stress are crucial in determining the suitability of materials for a particular application.
What are the Applications of Mechanical Seal?
Pump
Pumps represent one of the primary applications for mechanical shaft seals. In various industrial and commercial applications, pumps are used to transfer liquids or gases from one location to another. Mechanical shaft seals provide essential sealing at the rotating shaft of pumps, preventing the leakage of liquids or gases.From common pump standards like DIN and ANSI to the API 682 4th edition set by the American Petroleum Institute (API), corresponding standard dimensions exist.
DIN/ANSI Cartridge Mechanical Seals:
Single Cartridge Seal CarLife®99™
Dual Cartridge Seal CarLife®699™
API 682 Cartridge Mechanical Seals:
Single Cartridge Seal APD®155
Dual Cartridge Seal APD®302ODM Customized Mechanical Shaft Seals for Specific Pump Brands:
WARMAN® Rubber-Lined Slurry Pumps Seal APT302WM
Viking® Gear Pump Seal VK302
Sulzer® High-Performance Process Pump Seal SU99/SU299
Mixer, Agitator, Reactor
In industries such as chemical processing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, mixers are utilized for blending various chemical substances or serving as chemical reaction vessels or drying and compression equipment. These mixers often have large shaft diameters and produce significant torque, leading to substantial vibrations and swings during operation. Hence, the mechanical shaft seal serving as a sealing component requires enhanced strength and robustness, capable of withstanding prolonged extreme operating conditions and misalignment.Mixer seals ensure that the rotating components of mixers do not leak substances and prevent external contaminants from polluting the substances. This is crucial in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, ensuring hygiene, maintaining a safe operational environment, and stabilizing the mixing process.
Applied Mechanical Seals:
Single Cartridge Mixer Seal MGS99
Double Cartridge Mixer Seal MGS2000
Non-Contact Cartridge Mixer Seal GSB300
Compressor, Fan, Steam Turbine
In these applications, fluids primarily consist of gases. Air compressors pressurize gases to the desired pressure, while mechanical fans circulate air and regulate temperatures. Steam turbines are critical equipment in power plants or factories, utilizing high-speed rotating impellers to drive gases. Mechanical shaft seals play a vital role in these gas applications, ensuring that gases or high-temperature steam do not leak and simultaneously maintaining equipment efficiency and safe operation.Applied Gas Seals:
Non-Contact Single Cartridge Gas Seal FBG120
Non-Contact Dual Cartridge Gas Seal FBG220
Cartridge Gas Seal specifically for Steam Turbines STG170
2023-12-07